Top of the pageCheck Your Symptoms
Finger, Hand, and Wrist Problems, Noninjury
Topic Overview
Everyone has had a minor problem with a finger, hand, or wrist. Most of the time our body movements do not cause problems, but it's not surprising that symptoms occur from everyday wear and tear or from overuse. Finger, hand, or wrist problems can also be caused by injuries or the natural process of aging.
Your fingers, hands, or wrists may burn, sting, or hurt, or feel tired, sore, stiff, numb, tingly, hot, or cold. Maybe you can't move them as well as usual, or they are swollen. Perhaps your hands have turned a different color, such as red, pale, or blue. A lump or bump might have appeared on your wrist, palm, or fingers. Home treatment is often all that is needed to relieve your symptoms.
Finger, hand, or wrist problems may be caused by an injury. If you think an injury caused your problem, see the topic Finger, Hand, and Wrist Injuries. But there are many other causes of finger, hand, or wrist problems.
Overuse problems
- Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by pressure on a nerve (median nerve) in the wrist. The symptoms include tingling, numbness, weakness, or pain of the fingers and hand.
- Tendon pain is actually a symptom of tendinosis, a series of very small tears (microtears) in the tissue in or around the tendon. In addition to pain and tenderness, common symptoms of tendon injury include decreased strength and movement in the affected area.
- De Quervain's disease can occur in the hand and wrist when tendons and the tendon covering (sheath) on the thumb side of the wrist swell and become inflamed. See a picture of de Quervain's disease.
- Repetitive motion syndrome is a term used to describe symptoms such as pain, swelling, or tenderness that occur from repeating the same motion over and over.
- Writer's cramps develop with repeated hand or finger motion, such as writing or typing.
- Trigger finger or trigger thumb occurs when the flexor tendon and its sheath in a finger or thumb thicken or swell.
Bone, muscle, or joint problems
- Dupuytren's disease is an abnormal thickening of tissue beneath the skin in the palm of the hand or hands and occasionally the soles of the feet. The thickened skin and tendons (palmar fascia) may eventually limit movement or cause the fingers to bend so that they can't be straightened. See a picture of Dupuytren's contracture.
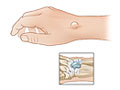
- Ganglion cysts are small sacs (cysts) filled with clear, jellylike fluid that often appear as bumps on the hands and wrists but can also develop on feet, ankles, knees, or shoulders. See a picture of a ganglion.
Problems from medical conditions
- Tingling or pain in the fingers or hand (especially the left hand) may be signs of a heart attack.
- Diabetes may change how the hands normally feel or sense touch. Decreased feeling in the hands is common because of decreased blood flow to the hands or damage to nerves of the hand.
- Pregnancy may cause redness, itching, swelling, numbness, or tingling that often goes away after delivery.
- Osteoarthritis is the progressive breakdown of the tissue that protects and cushions joints (cartilage). It may cause stiffness and pain with movement.
- Rheumatoid arthritis may cause stiffness and pain with movement. Over time, deformity of the fingers may occur. See a picture of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Lupus is a long-lasting autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks normal body tissues as though they were foreign substances. It may cause joint pain.
- Gout is an inflammatory joint disease that causes acute pain and swelling. It is a form of arthritis that develops when uric acid crystals form in and around the joints, commonly affecting the big toe joint.
- Raynaud's phenomenon is a condition in which some areas of the body, usually the fingers or toes, have an extreme response to cold temperature or emotional stress. During an attack of Raynaud's, the blood vessels in the affected areas tighten, severely limiting the flow of blood to the skin, causing numbness, tingling, swelling, pain, and pale color.
- Infection can cause pain, redness, and swelling that occur with red streaking, heat, fever, or the drainage of pus. An infection often causes tenderness to the touch or pain with movement at the site of the infection.
Check your symptoms to decide if and when you should see a doctor.
Check Your Symptoms
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, herbal remedies, and supplements can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
Symptoms of infection may include:
- Increased pain, swelling, warmth, or redness in or around the area.
- Red streaks leading from the area.
- Pus draining from the area.
- A fever.
Pain in adults and older children
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that you can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt your normal activities and your sleep, but you can tolerate it for hours or days. Moderate can also mean pain that comes and goes even if it's severe when it's there.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): You notice the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt your sleep or activities.
When an area turns blue, very pale, or cold, it can mean that there has been a sudden change in the blood supply to the area. This can be serious.
There are other reasons for color and temperature changes. Bruises often look blue. A limb may turn blue or pale if you leave it in one position for too long, but its normal color returns after you move it. What you are looking for is a change in how the area looks (it turns blue or pale) and feels (it becomes cold to the touch), and this change does not go away.
Pain in children under 3 years
It can be hard to tell how much pain a baby or toddler is in.
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the baby cannot sleep, cannot get comfortable, and cries constantly no matter what you do. The baby may kick, make fists, or grimace.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The baby is very fussy, clings to you a lot, and may have trouble sleeping but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The baby is a little fussy and clings to you a little but responds when you try to comfort him or her.
Pain in children 3 years and older
- Severe pain (8 to 10): The pain is so bad that the child can't stand it for more than a few hours, can't sleep, and can't do anything else except focus on the pain. No one can tolerate severe pain for more than a few hours.
- Moderate pain (5 to 7): The pain is bad enough to disrupt the child's normal activities and sleep, but the child can tolerate it for hours or days.
- Mild pain (1 to 4): The child notices and may complain of the pain, but it is not bad enough to disrupt his or her sleep or activities.
Certain health conditions and medicines weaken the immune system's ability to fight off infection and illness. Some examples in adults are:
- Diseases such as diabetes, cancer, heart disease, and HIV/AIDS.
- Long-term alcohol and drug problems.
- Steroid medicines, which may be used to treat a variety of conditions.
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer.
- Other medicines used to treat autoimmune disease.
- Medicines taken after organ transplant.
- Not having a spleen.
Seek Care Today
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an
ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Make an Appointment
Based on your answers, the problem may not improve without medical care.
- Make an appointment to see your doctor in the next 1 to 2 weeks.
- If appropriate, try home treatment while you are waiting for the appointment.
- If symptoms get worse or you have any concerns, call your doctor. You may need care sooner.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Home Treatment
Home treatment may be all that is needed for a finger, hand, or wrist problem.
- Remove all rings, bracelets, watches, or any other jewelry from your finger, wrist, or arm as soon as you notice swelling. It will be harder to remove the jewelry after swelling increases.
- Use rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) for pain and swelling.
- Treat hands sensitive to cold by avoiding and protecting your hands from the cold.
- Avoid sleeping on your hands, which may decrease blood flow to your fingers.
- Treat blisters on fingers or hands.
- Stop, change, or take a break from your activities.
|
Try a nonprescription medicine to help treat your pain: |
|---|
Talk to your child's doctor before switching back and forth between doses of acetaminophen and ibuprofen. When you switch between two medicines, there is a chance your child will get too much medicine. |
|
Be sure to follow these safety tips when you use a nonprescription medicine: |
|---|
|
Symptoms to watch for during home treatment
Call your doctor if any of the following occur during home treatment:
- Pain or swelling develops.
- Signs of infection develop.
- Numbness; tingling; or cool, pale skin develops.
- Symptoms continue despite home treatment.
- Symptoms become more severe or frequent.
Prevention
The following tips may prevent finger, hand, and wrist problems.
General tips
- Do exercises that strengthen your hand and arm muscles.
- Stop, change, or take a break from activities that cause your symptoms.
- Reduce the speed and force of repetitive movements in activities such as hammering, typing, knitting, quilting, sweeping, raking, playing racquet sports, or rowing.
- Change positions when holding objects, such as a book or playing cards, for any length of time.
- Use your whole hand to grasp an object. Gripping with only your thumb and index finger can stress your wrist.
- When you work with tools that vibrate, consider using special gloves that support the wrist and have vibration-absorbing padding.
- Wear protective gear, such as wrist guards, in sports activities.
Protect your hands from cold
- Wear gloves anytime it is cool outside.
- Use an insulated cover when you drink from a cold glass.
- Avoid caffeine (coffee, cola, tea, chocolate) and tobacco products. Nicotine and caffeine cause blood vessels to narrow, which decreases blood flow to the hands.
- Eat a hot meal before going out. Eating raises your body temperature and helps keep you warm.
Work posture and body mechanics
- Organize your work so that you can change your position occasionally while maintaining a comfortable posture.
- Position your work so you do not have to turn excessively to either side.
- Keep your shoulders relaxed when your arms are hanging by your sides.
- When using a keyboard, keep your forearms parallel to the floor or slightly lowered and keep your fingers lower than your wrists. Allow your arms and hands to move freely. Take frequent breaks to stretch your fingers, hands, wrist, shoulders, and neck. If you use a wrist pad during breaks from typing, it's best to rest your palm or the heel of your hand on the support, rather than your wrist.
Preparing For Your Appointment
You can help your doctor diagnose and treat your condition by being prepared to answer the following questions:
- What are your main symptoms? How long have you had your symptoms?
- Have you had this problem in the past? If so, do you know what caused the problem at that time? How was it treated? What do you think is causing your symptoms now?
- What activities make your symptoms better or worse? Have you started any new activities, sports, or training techniques?
- Do you think that activities related to your job or hobbies caused your symptoms?
- What home treatment have you tried? Did it help?
- What nonprescription medicines have you tried? Did they help?
- Have you started any new medicines, or have you had a change in the dosage of a medicine?
- Do you have any health risks?
Related Information
Credits
ByHealthwise Staff
Primary Medical Reviewer William H. Blahd, Jr., MD, FACEP - Emergency Medicine
Kathleen Romito, MD - Family Medicine
Adam Husney, MD - Family Medicine
Current as ofNovember 20, 2017
- Top of Page
Next Section:
Check Your Symptoms
Previous Section:
Topic Overview- Top of Page
Next Section:
Home Treatment
Previous Section:
Check Your Symptoms- Top of Page
Next Section:
Prevention
Previous Section:
Home Treatment- Top of Page
Next Section:
Preparing For Your Appointment
Previous Section:
Prevention- Top of Page
Next Section:
Related Information
Previous Section:
Preparing For Your Appointment- Top of Page
Next Section:
Credits
Previous Section:
Related Information- Top of Page
Current as of: November 20, 2017