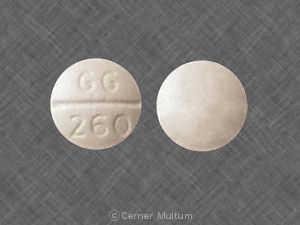
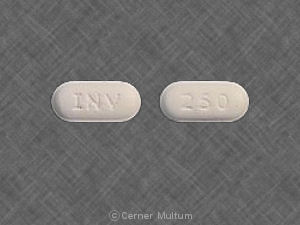
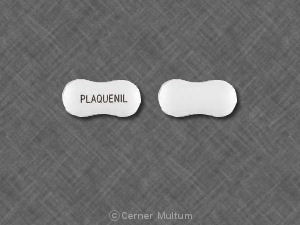
What is the most important information I should know about hydroxychloroquine?
Taking hydroxychloroquine long-term or at high doses may cause irreversible damage to the retina of your eye. Stop taking hydroxychloroquine and call your doctor at once if you have trouble focusing, if you see light streaks or flashes in your vision, or if you notice any swelling or color changes in your eyes.
What is hydroxychloroquine?
Hydroxychloroquine is used to treat or prevent malaria, a disease caused by parasites that enter the body through the bite of a mosquito. Malaria is common in areas such as Africa, South America, and Southern Asia. This medicine is not effective against all strains of malaria.
Hydroxychloroquine is also used to treat symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and discoid or systemic lupus erythematosus.
Hydroxychloroquine may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
What should I discuss with my health care provider before taking hydroxychloroquine?
You should not use hydroxychloroquine if you are allergic to it.
Hydroxychloroquine should not be used for long-term treatment in children.
To make sure hydroxychloroquine is safe for you, tell your doctor if you have:
- a history of vision changes or damage to your retina caused by an anti-malaria medication;
- heart disease, heart rhythm disorder (such as long QT syndrome);
- diabetes;
- a stomach disorder;
- an allergy to quinine;
- liver or kidney disease;
- psoriasis;
- alcoholism; or
- a genetic enzyme disorder such as porphyria or glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency.
It is not known whether this medicine will harm an unborn baby. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
Malaria is more likely to cause death in a pregnant woman. If you are pregnant, talk with your doctor about the risks of traveling to areas where malaria is common.
It is not known whether hydroxychloroquine passes into breast milk or if it could harm a nursing baby. Tell your doctor if you are breast-feeding a baby.
Hydroxychloroquine is not approved for use by anyone younger than 18 years old.
How should I take hydroxychloroquine?
Follow all directions on your prescription label. Do not take this medicine in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended. Hydroxychloroquine is sometimes given only once per week. Choose the same day each week to take this medicine if you are on a weekly dosing schedule.
Take hydroxychloroquine with a meal or a glass of milk.
To prevent malaria: Start taking the medicine 2 weeks before entering an area where malaria is common. Continue taking the medicine regularly during your stay and for at least 8 weeks after you leave the area.
To treat malaria: Hydroxychloroquine is usually given for 3 days, starting with one high dose followed by a smaller dose during the next 2 days in a row.
Take this medicine for the full prescribed length of time for malaria. Your symptoms may improve before the infection is completely cleared.
Use protective clothing, insect repellents, and mosquito netting around your bed to further prevent mosquito bites that could cause malaria.
Call your doctor as soon as possible if you have been exposed to malaria, or if you have fever or other symptoms of illness during or after a stay in an area where malaria is common.
No medication is 100% effective in treating or preventing all types of malaria. For best results, keep using the medication as directed. Talk with your doctor if you have fever, vomiting, or diarrhea during your treatment.
When treating lupus or arthritis, hydroxychloroquine is usually given daily for several weeks or months. For best results, keep using the medication as directed. Talk with your doctor if your symptoms do not improve after 6 months of treatment.
While using hydroxychloroquine, you may need frequent blood tests and vision exams.
Store at room temperature away from moisture, heat, and light.
What happens if I miss a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your next scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up the missed dose.
What happens if I overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. An overdose of hydroxychloroquine can be fatal, especially in children.
Hydroxychloroquine overdose must be treated quickly. You may be told to induce vomiting right away (at home, before transport to an emergency room). Ask the poison control center how to induce vomiting in the case of an overdose.
Overdose symptoms may include drowsiness, vision changes, slow heart rate, chest pain, severe dizziness, seizure (convulsions), or shallow breathing.
What should I avoid while taking hydroxychloroquine?
Avoid taking an antacid or Kaopectate (kaolin-pectin) within 4 hours before or after you take hydroxychloroquine. Some antacids can make it harder for your body to absorb hydroxychloroquine.
What are the possible side effects of hydroxychloroquine?
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Taking hydroxychloroquine long-term or at high doses may cause irreversible damage to the retina of your eye. Stop taking hydroxychloroquine and call your doctor at once if you have trouble focusing, if you see light streaks or flashes in your vision, or if you notice any swelling or color changes in your eyes.
Call your doctor at once if you have:
- headache with chest pain and severe dizziness, fainting, fast or pounding heartbeats;
- very slow heart rate, weak pulse;
- muscle weakness, numbness or tingling;
-
low blood sugar --headache, hunger, sweating, irritability, dizziness, nausea, fast heart rate, and feeling anxious or shaky; or
-
low blood cell counts --fever, chills, sore throat, weakness or ill feeling, swollen gums, mouth sores, skin sores, rapid heart rate, pale skin, easy bruising, unusual bleeding, feeling light-headed.
Common side effects may include:
- headache, dizziness, ringing in your ears;
- nausea, vomiting, stomach pain;
- loss of appetite, weight loss;
- mood changes, feeling nervous or irritable;
- skin rash or itching; or
- hair loss.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What other drugs will affect hydroxychloroquine?
Hydroxychloroquine can cause serious liver or heart problems, especially if you use certain medicines at the same time, including:
- other medicines to treat malaria;
- an antibiotic or antifungal medicine;
- antiviral medicine to treat hepatitis or HIV/AIDS;
- antidepressants or antipsychotic medicines;
- birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy;
- cancer medication;
- cholesterol-lowering medication;
- heart or blood pressure medicine;
- pain or arthritis medicines (including aspirin, Tylenol, Advil, and Aleve);
- seizure medication;
- stomach acid reducers; or
- tuberculosis medicine.
This list is not complete and many other drugs can interact with hydroxychloroquine. This includes prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Not all possible interactions are listed in this medication guide. Tell your doctor about all medicines you use, and those you start or stop using during your treatment with hydroxychloroquine. Give a list of all your medicines to any healthcare provider who treats you.
Where can I get more information?
Your pharmacist can provide more information about hydroxychloroquine.
Remember, keep this and all other medicines out of the reach of children, never share your medicines with others, and use this medication only for the indication prescribed.
Every effort has been made to ensure that the information provided by Cerner Multum, Inc. ('Multum') is accurate, up-to-date, and complete, but no guarantee is made to that effect. Drug information contained herein may be time sensitive. Multum information has been compiled for use by healthcare practitioners and consumers in the United States and therefore Multum does not warrant that uses outside of the United States are appropriate, unless specifically indicated otherwise. Multum's drug information does not endorse drugs, diagnose patients or recommend therapy. Multum's drug information is an informational resource designed to assist licensed healthcare practitioners in caring for their patients and/or to serve consumers viewing this service as a supplement to, and not a substitute for, the expertise, skill, knowledge and judgment of healthcare practitioners. The absence of a warning for a given drug or drug combination in no way should be construed to indicate that the drug or drug combination is safe, effective or appropriate for any given patient. Multum does not assume any responsibility for any aspect of healthcare administered with the aid of information Multum provides. The information contained herein is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, warnings, drug interactions, allergic reactions, or adverse effects. If you have questions about the drugs you are taking, check with your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
Copyright 1996-2018 Cerner Multum, Inc. Version: 8.02. Revision date: 12/5/2017.