Insulin Pump
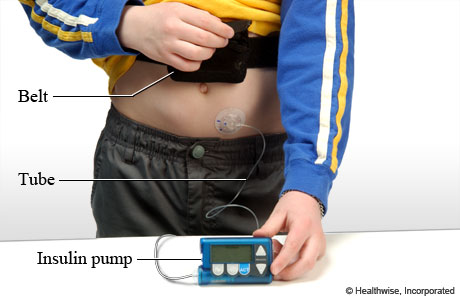
An insulin pump is a small computerized device that delivers insulin into the body. This is different from injecting insulin throughout the day using insulin syringes and needles.
Insulin pumps can be programmed to deliver very precise amounts of insulin in a continuous (basal) dose and in carefully planned extra (bolus) doses delivered at specific times throughout the day, usually when eating.
Some pumps, like the one in this picture, connect to the body through a thin tube and needle inserted under the skin, usually in the abdomen. Some pumps attach directly to the body and do not need tubing. Some pump systems use a remote control. And some pumps are disposable and do not use tubing or a remote control. A pump with no tubing is sometimes called a "pump patch."
Most pumps can hold between 200 and 300 units of insulin, depending on the model used. Some pumps also work as a blood glucose meter or communicate with your meter to adjust your bolus dose of insulin.
Insulin pumps allow flexibility in how a person times his or her meals and snacks. The pumps may help some people to have fewer low blood sugar events (hypoglycemic episodes) than people who inject insulin. The insulin pump is designed to mimic the normal function of the pancreas.
Current as of: December 7, 2017
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review: Kathleen Romito, MD - Family Medicine & Adam Husney, MD - Family Medicine