Carrier Test for Autosomal Recessive Conditions
Autosomal recessive conditions are genetic diseases that are passed to a child through both parents' chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases include Tay-Sachs disease, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), and phenylketonuria (PKU).
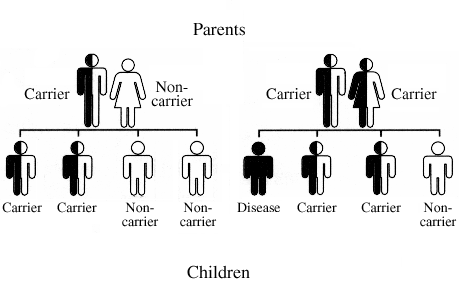
Each person inherits 23 chromosomes from each parent and so has 23 pairs of chromosomes. Each chromosome contains genes. One or both of the genes in a pair can carry a mutation and fail to function properly. In an autosomal recessive condition, both chromosomes in a pair must have a mutation for the person to have the disease. If only one gene carries a mutation, the person is a carrier of the condition but does not have any symptoms.
| One parent is a carrier | Both parents are carriers |
|---|---|
If only one parent carries a mutation, there is:
| If both parents carry a mutation, there is:
|
Current as of: October 9, 2017
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review: Kathleen Romito, MD - Family Medicine & Martin J. Gabica, MD - Family Medicine & Adam Husney, MD - Family Medicine & Siobhan M. Dolan, MD, MPH - Reproductive Genetics